48
Annual Report
2013
Power Industry and Competition
Global Power Situation
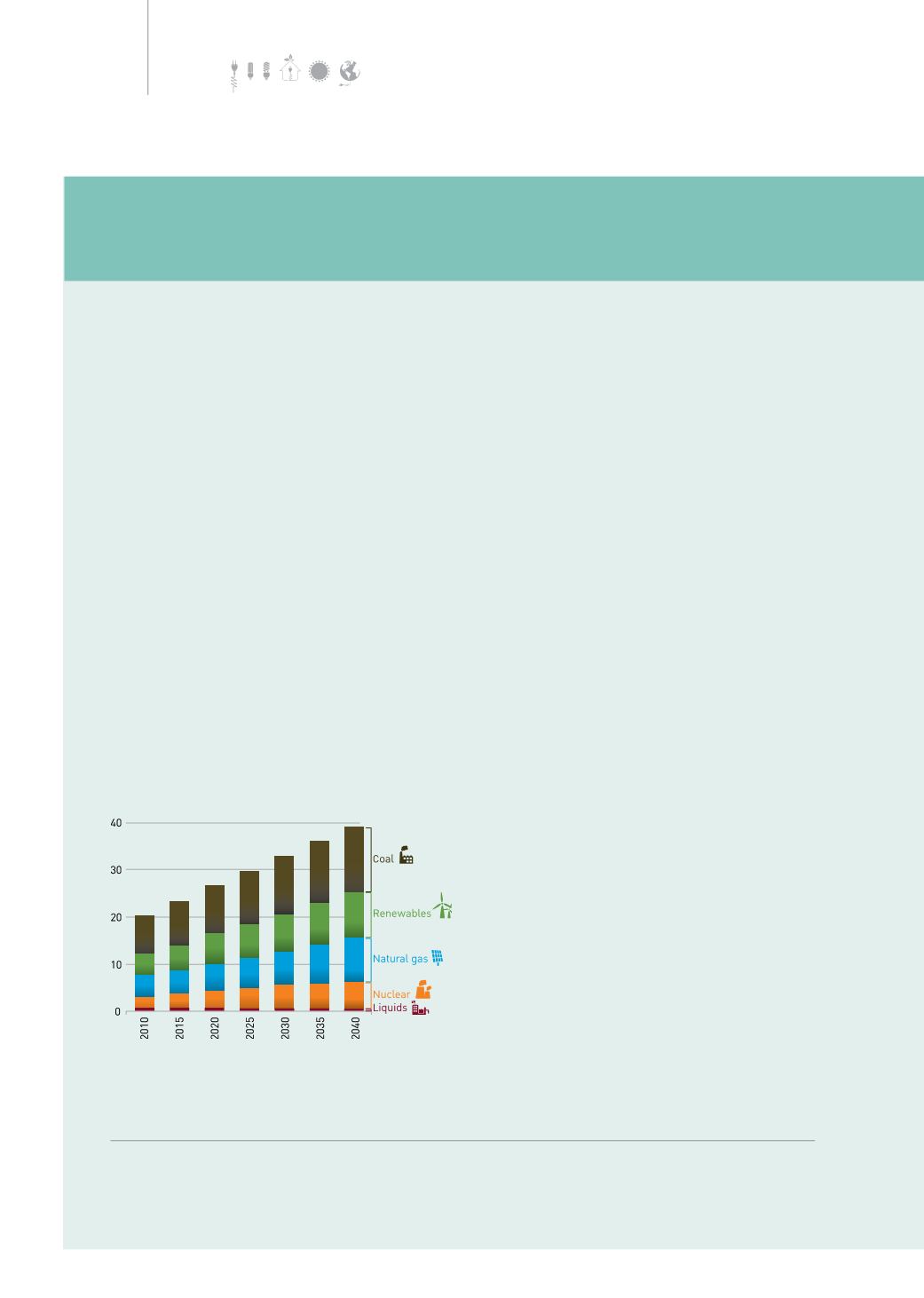
IEO2013
1
projected that from 2010-2040 world
energy consumption will increase from 20.0 trillion
KW-hours to 39.0 trillion KW-hours. Global demand
for energy will grow by 2.2 per cent per annum on
average. Energy consumption in OECD
2
countries
grow at a slower rate than non-OECD
3
countries.
Non-OECD Asian countries leading by China and
India, is the world’s fastest growing electricity
generating region at 3.6 per cent growth per
annum, contributing to 44 per cent of the total
global output.
At present, the most-used fuel for electricity
generating is coal. In 1970’s, nuclear power
became important sources of energy for electricity
generation. Later in 1980’s natural gas was heavily
used to generate power. Since 1970’s the use of oil
as the energy source for electricity generation has
declined because of the rapidly increasing price.
Global electricity generation by type of fuel
from 2010-2040 (trillion KW-Hours)
Source: International Energy Outlook 2013
Considering renewable energy used for power
production, from 2010-2040, renewable energy is
the fastest growing, especially non-hydro power
(e.g. wind power) whose market share expanded
to 9 per cent in 2040 from 4 per cent in 2010. The
second most use energy source is natural gas and
nuclear power, which will grow by 2.5 per cent per
year while coal grows slowly at 1.8 per cent per
annum. Coal, however, will remain the most-used
source of energy for electricity generation until
2040. Coal use trend might change drastically in
the future if international policy and agreement
related to greenhouse gas emission and limitation
are changed.
1. ElectricityConsumption inMajorMarkets
1) Market and competition in Commonwealth
of Australia
In the past five years, electricity consumption
inAustraliasloweddownduetosloweconomy
and industrial development, the increase
of household solar panels and the rise of
electricity price. The country shifted its focus
to solar and wind power as the major
sources of energy for electricity generation
and promoted clean energy power plants.
Australia also introduced carbon tax, affecting
profitabilityof coal power plants.However,
such tax might be terminated in the
next 18-24 months under the new government.
1 International Energy Outlook 2013
2 Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is an international economic organization between developed
countries. Currently OECD has 34 members.
3 Non-OECD member countries


